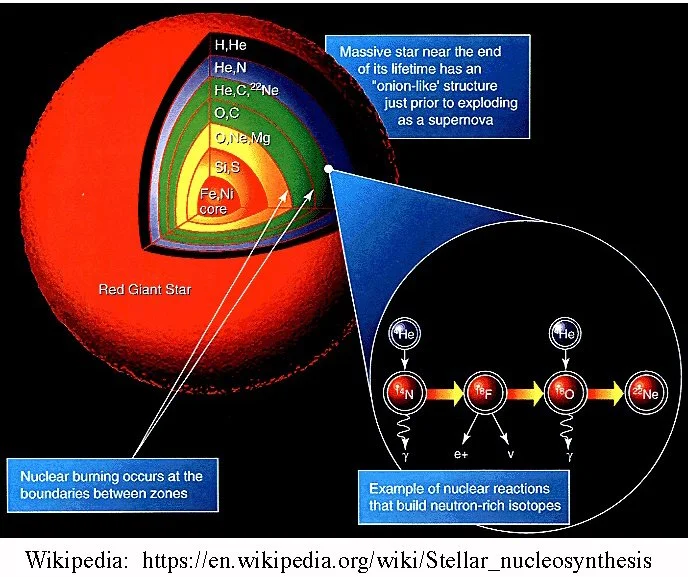
Shovel Point, Tettegouche State Park, Illgen City, MinnesotaIn the Beginning…
The Big Bang is a theory that describes the universe's expansion from an initial state of high density and temperature involving an abundance energy in the form of light, microwave radiation and cosmic inflation (accelerated expansion) during the earliest stage. This near instantaneous singularity happened 13.787±0.02 billion years ago.
The theory describes an extraordinarily hot and dense primordial universe existing for a short instant. Current day physics lacks a model adequate to describe the earliest conditions of the Big Bang; it is the best estimate created by the physics community to describe "the beginning". The theory hypothesizes that very quickly (within a few microseconds) the universe expanded to enhance cooling that allowed the formation of subatomic particles and atoms. These early elements—mostly hydrogen, helium and lithium—then coalesced under the force of gravity aided by dark matter, to form the early stars and galaxies. Measurements of the redshifts of supernovae indicate that the expansion of the universe is accelerating, an observation attributed to a concept called dark energy.
The earliest description of an expanding universe, known as Hubble's law, was published by physicist Edwin Hubble in 1929. This discerned that galaxies are moving away from Earth at a rate that accelerates proportionally with distance. In 1931 physicist Georges Lemaître proposed that the universe emerged from a "primeval atom", introducing the modern notion of the Big Bang. In 1964, cosmic radiation was discovered; this radiation was shown to be uniform over all directions in the sky and the shape of the energy versus intensity curve, both consistent with the Big Bang models of high temperatures and densities in the distant past.
However, there remain aspects of the observed universe that are not yet adequately explained by the Big Bang models. These include the unequal abundances of matter and antimatter, known as Baryon asymmetry, the detailed nature of dark matter surrounding galaxies, and the origin of dark energy.
Assumptions:
Big Bang cosmology models depend on three major assumptions: 1) The universality of physical laws, 2) the cosmological principle, (the notion that spatial distribution of matter in the universe is uniformly isotropic and homogeneous when viewed on a large enough scale) is maintained, and 3) matter content can be modeled as a perfect fluid. The universality of physical laws is one of the underlying principles of the theory of relativity. The cosmological principle states that on large scales the universe is homogeneous and isotropic—appearing the same in all directions regardless of location. A perfect fluid has no viscosity; the pressure of a perfect fluid is proportional to its density.
The first assumption has been tested by observations showing that the largest possible deviation of the fine-structure constant over much of the age of the universe is of order 10−5. The key physical law behind these models, general relativity has passed stringent tests on the scale of the Solar System and binary stars. The cosmological principle has been confirmed to a level of 10−5 via observations of the temperature of cosmic radiation. The universe has been measured to be homogeneous with an upper bound on the order of 10% inhomogeneity.
What is the role of Dark Matter and Dark Energy?
In the elegant words of a well known physicist, dark matter is the invisible glue that holds the universe together. This mysterious material is all around us, making up most of the matter in the universe. But what exactly is dark matter? That's a question that scientists have been trying to solve for more than 100 years.
Dark matter makes up most of the mass in galaxies and galaxy clusters. In fact, scientists estimate that ordinary matter makes up only about 5% of the universe, while dark matter makes up about 27%. (The rest is thought to be dark energy, which is its own mystery). It's thought that dark matter shapes the cosmos, organizing galaxies and cosmic objects on a large scale.
From stars and galaxies to the shoes on your feet, ordinary matter makes up everything we can see in the universe — in wavelengths spanning from the infrared to visible light and gamma rays. While dark matter interacts with ordinary matter through gravity, it does not seem to interact at all with the electromagnetic spectrum, including visible light. So dark matter doesn't absorb, reflect, or emit any light.
While dark matter is invisible, it does have some things in common with ordinary matter: It takes up space and it holds mass. Because of this, it interacts with and influences ordinary matter throughout the universe, which is how we're able to "see" and study dark matter. So, what can we see? And what have we seen that makes us so sure that dark matter exists?
Discovering Dark Matter
After noting this discrepancy, Zwicky suggested that there might be an invisible form of matter that created the gravity holding these galaxies together. While these early investigations sparked ideas and curiosity around dark matter, it was still seen as a fringe concept without sufficient evidence to support it.
That changed in the 1970s when American astronomer Vera Rubin observed this "missing matter" problem in spiral galaxies. Rubin looked at the stars on the outer edges of the spirals. To explain why these stars moved as fast as they did without flying into intergalactic space, there had to be a large amount of matter holding them in place. But, not seeing any of this matter, Rubin concluded that these galaxies must be held together by dark matter. Rubin's discovery provided such strong evidence for dark matter that the concept was embraced by the scientific community. Today, while not all astronomers agree on what dark matter might be, its existence is widely accepted.
Studying Dark Matter
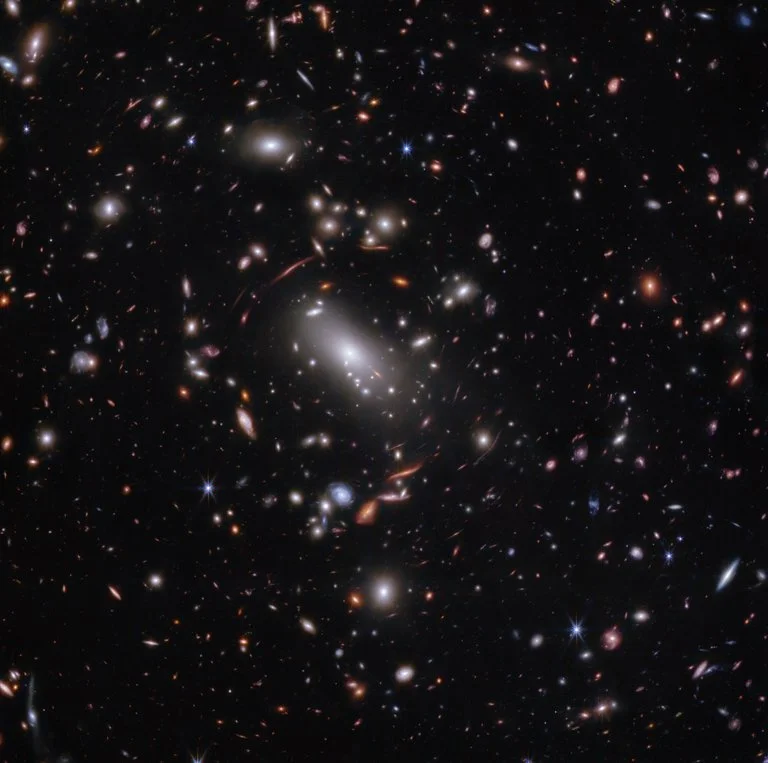
Today, scientists have even more direct evidence of dark matter. While dark matter doesn't interact with light, its gravity can bend light from distant galaxies, creating an effect called gravitational lensing. Studying galaxies distorted by gravitational lensing can help scientists better understand dark matter and its place in the universe.
In 2006, scientists observed the Bullet Cluster and discovered some of the best direct evidence for dark matter. This galaxy cluster, formally known as 1E 0657-56, was created when two large galaxy clusters collided in an extremely energetic event about 3.8 billion light-years from Earth.
During this collision, hot gas from one cluster interacted with hot gas from the other. In the image above, hot X-ray emitting gas made of normal matter and detected by NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory is shown in pink. The blue portions show the distribution of dark matter and were revealed using gravitational lensing observations taken by NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope and the Giant Magellan Telescope, which is operated by an international consortium. The blue areas represent most of the mass in these clusters and are distributed differently than the hot gas. Researchers think that this material is likely dark matter. So, in this image, you can see direct evidence of dark matter with your own eyes.
With sufficient evidence to support dark matter's existence, scientists are working hard to explore not only what dark matter is but also where it's distributed throughout the universe.
Taking Dark Matters Temperature
Because dark matter has mass, it also must have a temperature. For a while, scientists considered two options — cold dark matter made up of slow-moving particles and warm or hot dark matter made of faster-moving particles.
In simulations, scientists modeled how our universe would operate if dark matter was cold and slow or hot and fast. They showed that with cold dark matter, the universe’s structures appear to exist and move as they are observed in reality. When the simulations were done with warm or hot dark matter, however, cosmic structures don't seem able to stick together and can't exist in the ways we observe.
Based on such simulations, scientists currently agree that it is most likely that whatever dark matter is, it is cold or slow-moving. It's additionally thought that this cold dark matter formed in the early universe with a low enough velocity to allow galaxies to form and distribute as we see them today.
Leading Dark Matter Candidates
There are currently many proposed explanations for what makes up dark matter. In fact, scientists think it's possible that dark matter is made up of more than one kind of matter or particle.
Below are a few of the current candidates with the most support from the scientific community. For context, scientists have been searching for these candidates but have not yet found evidence which would confirm any candidate. New candidates may also continue to emerge.
WIMPs (Weakly Interacting Massive Particles)
WIMPs are hypothetical particles that are big, heavy, and slow-moving. They don't absorb or emit light or strongly interact with any other particles that we've seen so far. Scientists think WIMPs interact with gravity and possibly other forces, but in a way that allows these particles to pass through normal matter almost seamlessly. When WIMPs interact with each other, however, they may cancel each other out. That destruction could produce gamma rays. Scientists are currently searching through data from NASA's Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope to look for signatures of WIMPs interacting and annihilating one another.
Axions
Axions are hypothetical subatomic particles scientists think are both low-mass and low-energy. This particle was first theorized in 1977 as a solution to a fundamental problem within particle physics called the strong CP problem. (CP stands for charge conjugation symmetry and parity symmetry.) In essence, the problem is that when regular matter particles are inverted or swapped with antimatter particles, the laws of physics should remain the same, and the particles should be symmetrical and cancel out. This would mean that in the first moments of the universe, matter and antimatter should have canceled each other out. But that didn't happen. Scientists proposed axions as a hypothetical particle that could solve the strong CP problem by violating this symmetry to allow regular matter to flourish. Scientists think that these hypothetical particles could be dark matter and have found additional evidence for the existence of axions over the years. Scientists have also used data from NASA telescopes including Fermi, Chandra, and NuSTAR (Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array) to search for evidence of axion oscillations in X-ray and gamma-ray observations.
Primordial black holes
Black holes are the densest objects in the universe with gravity so extreme that at a certain point not even light can escape. Primordial black holes are hypothetical black holes scientists think formed right after the birth of the universe. Primordial black holes could be as small as an atom or as large as a supermassive black hole, with possible masses ranging from 100,000 times less massive than a paperclip to 100,000 times more massive than the Sun. Recent studies suggest a primordial black hole could travel through our solar system once every 10 years, which may allow scientists to eventually study them directly. One theory, proposed by physicist Stephen Hawking, suggests that after primordial black holes formed from regular matter at the start of the universe, they collapsed, becoming dark matter that spread out across the universe. Scientists use data from Fermi to search for primordial black hole evaporation.
Dark Matter versus Dark Energy
Dark matter often causes confusion because of its name. Dark matter is not a dark color. Rather, it's called “dark” because it's invisible to us since it doesn't absorb, reflect, or emit any light.
Another misconception about dark matter relates to dark energy. While the two are both cosmic mysteries with "dark" in their name, they are not the same thing. Dark matter is a mysterious type of matter that holds galaxies together. Dark energy is the name scientists have given to whatever is causing our universe to expand at an accelerating rate over time — a cosmic mystery. Dark energy isn't concentrated in galaxies or galaxy clusters, instead scientists think it’s spread throughout the universe.
Both dark matter and dark energy pose deep, unanswered questions about the universe. Although they are distinct phenomena, scientists map the distribution of dark matter to help us understand the universe's accelerated expansion which is caused by dark energy.
Reference:
Excerpt from https://science.nasa.gov/dark-matter/ written by Chelsea Gohd, NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory Aug 28, 2025